The Means by Which a Pathogenic Organism Invades the Body
Pathogens are of different types and they can spread by various means but most commonly they spread by means of skin contact or while transferring body fluids or through contaminated surface contacting. Pathogens are infectious micro-organisms germs or biological agents that cause infectious diseases or illnesses in the host human.
Or commensals these bacteria usually cause no harm but can invade other sites of the body and give rise infections.
. The general lack of internal membranes in bacteria means these reactions. What are viral or bacteria germs that invade body cells called. Virus bacterium fungus protozoa and helminth.
The trypanosome is coated with a single type of glycoprotein the variant-specific glycoprotein VSG which elicits a potent protective antibody response that rapidly clears most of the parasites. Aureus and almost never associated with nonpathogenic S. Pathogens which include bacteria protists fungi and other infectious organisms can be found in food and water on surfaces and in the air.
A CSF sample is obtained by a physician usually via lumbar puncture or spinal tap. The term host is refers to those organisms or animals that harbors a pathogen it means that the host will provide nutrients and shelter to the pathogen. Epidermidis which has led to much speculation as to its role as a determinant.
For example animals playing host to parasitic worms. Macrophages respond to these calls and invade the site of infection consuming any cell-free or cell-associated pathogen. Any foreign substance introduced into the body that provokes an immune response.
Your body can be more prone to bacterial infections when your immune system is compromised by a virus. Coagulase activity is almost always associated with pathogenic S. This article is confined to human microbial pathogens although plant and animal pathogens are also widespread in nature.
Infection occurs when viruses bacteria or other microbes enter your body and begin to multiply. This mucus is mainly composed of glycoproteins called mucins digestive enzymes antimicrobial peptides and immunoglobulins. A host is the organism that is invaded and often harmed by a pathogen.
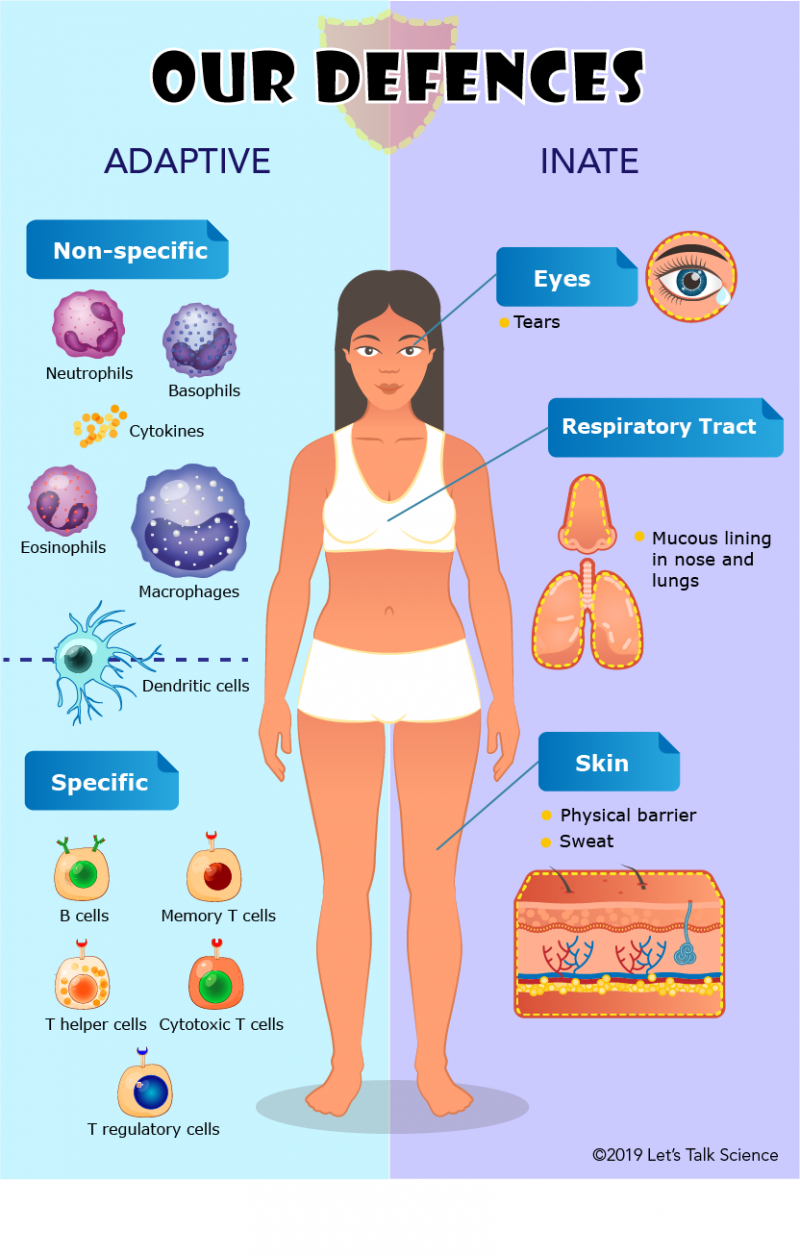
The body has defence mechanisms that enable it to resist microbial invasion of its tissues and give it a natural immunity or innate resistance against many microorganisms. The means by which a pathogenic organism invades the body. When a pathogenic microorganism bacterium virus or protozoal parasite infects the human body a battle ensues between the hosts innate adaptive.
The ability of a pathogen to cause disease is called pathogenicity. Trypanosomes are insect-borne protozoa that replicate in the extracellular tissue spaces of the body and cause sleeping sickness in humans. The power of an organism to overcome body defenses and cause disease.
Viruses Smaller than bacteria a virus invades a host cell. Host pathogen interaction means how a pathogen will survive within a host body weather it causes disease or not. Viruses bacteria and so on are called germs infective agents microbes pathogens and so forth.
Parasites are quite common and can cause a range of issues such as weight loss rash sleeping problems upset digestive system and more. The most common type of pathogens are bacteria viruses and fungi. The intestinal mucus layer for example plays a key role in limiting invasion by commensal bacteria of the microflora or by foodborne pathogenic bacteria Fig.
Parasites are organisms that can invade the body. The trypanosome genome however. The severity of the disease state depends upon its virulence.
Concern over pathogens is one of the main reasons that we wash our hands after going to the bathroom or touching raw meat. Coagulase formed by Staphylococcus aureus is a cell-associated and diffusible enzyme that converts fibrinogen to fibrin which causes clotting. There are three common types of Parasites that often cause issues in humans.
The needle is inserted into the spinal canal in your lower back to collect CSF for testing. Any microorganism which is able to cause disease in a host organism is termed a pathogen. The degree to which an organism is pathogenic is called virulence.
Once a pathogenic organism has been isolated it can be further. Pathogenic bacteria are specially adapted and endowed with mechanisms for overcoming the normal body defences and can invade parts of the body such as the blood where. A pathogen is defined as an infectious microorganism present in the natural environments that can infect or invades the body and causes the disease to its host.
Some pathogens exist as air borne particles. The process of reducing the virulence of a pathogen to prepare a vaccine. Once youre infected viruses invade host cells within your body.
These pathogens are then destroyed by internal mechanisms in the. The disease state caused by a virus enables normally harmless bacteria to. There are five main types of pathogens.
Escherichia coli is a commensal in the human gut but can. In the body there are many types of harmless bacteria and some may even support essential bodily functions. It can be cellular such as bacteria protozoa parasites fungi or acellular such as virus and prion.
No comments for "The Means by Which a Pathogenic Organism Invades the Body"
Post a Comment